As of GGSN Release 3.0, the Cisco Systems GGSN supports virtual APN access from the GPRS PLMN using the virtual access point type on the GGSN. The virtual APN feature on the GGSN allows multiple users to access different physical target networks through a shared APN access point on the GGSN.
In a GPRS network, the user APN information must be configured at several of the GPRS network entities, such as the HLR and DNS server. In the HLR, the user subscription data associates the IMSI (unique per user) with each APN that the IMSI is allowed to access. At the DNS server, APNs are correlated to the GGSN IP address. If DHCP or RADIUS servers are in use, the APN configuration can extend to those servers too.
The virtual APN feature reduces the amount of APN provisioning required by consolidating access to all real APNs through a single virtual APN at the GGSN. Therefore, only the virtual APN needs to be provisioned at the HLR and DNS server, instead of each of the real APNs to be reached. The GGSN also must be configured for the virtual APN.
The Cisco Systems GGSN software determines the ultimate target network for the session by receiving the create PDP context request at the virtual access point and extracting the domain name to direct the packet to the appropriate real APN. The real APN is the actual destination network.

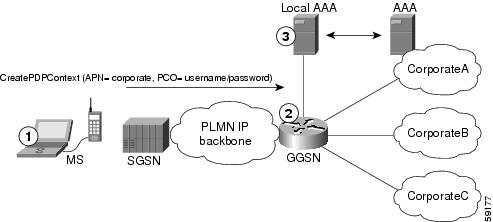
| 1. | At the MS, the user connects to the network with a username in the form of login@domain, such as ciscouser@CorporateA.com. The SGSN sends a create PDP context request to the GGSN using the virtual APN of "corporate." The create PDP context also includes the username in login@domain format in the protocol configuration option (PCO) information element. |
| 2. | The GGSN extracts the domain from the information in the PCO, which corresponds to the real target network on the GGSN. In this example, the GGSN finds CorporateA.com as the domain and directs the session to the appropriate real APN for the target network. In this case, the real APN is corporateA.com. The GGSN uses the complete username to do authentication. |
| 3. | The local or corporate AAA server is selected based on the domain part of the username, which is CorporateA.com in this case. |
Benefits of the Virtual APN Feature
The virtual APN feature provides the following benefits:
•![]() Simplifies provisioning of APN information at the HLR and DNS servers.
Simplifies provisioning of APN information at the HLR and DNS servers.
•![]() Improves scalability for support of large numbers of corporate networks, ISPs, and services.
Improves scalability for support of large numbers of corporate networks, ISPs, and services.
•![]() Increases flexibility of access point selection.
Increases flexibility of access point selection.
•![]() Eases deployment of new APNs and services.
Eases deployment of new APNs and services.
简单来说,传统的实现是,在GGSN上可能要配置很多APN,包括很多企业APN。同样,在HLR、DNS还有RADIUS也要有相应的APN配置,同时如果MS签约了多个APN的话,则需要在手机中每次指定访问的APN。有了虚拟APN的话,GGSN还有HLR、DNS这些节点都只需要配置一个虚拟APN就可以了,而不用配置实际的APN。假设原来GGSN要配置10个真实的APN,那HLR、DNS也要配10个。用户如果都签约了,也要有10个APN存在手机。但现在,所有的节点包括用户都只需要配置一个虚拟APN就够了。激活请求送给GGSN后,GGSN帮你做翻译,送给实际的物理APN对应的PDN网络。所以最大的好处上面也写了,就是可以简化网络侧和用户的配置、以及利于新APN新业务的开通。
别名APN:(下面的话来自阿尔卡特的GGSN广告)
单一APN管理。iGGSN可以实现APN翻译功能。GPRS用户只要在手机上设定一个APN别名,当用户request一项业务时,iGGSN就能通过用户的签约信息,翻译出该用户所能使用的业务。单一APN管理大大降低了GPRS手机的操作复杂度和对用户的要求。
| 欢迎光临 51学通信技术论坛 (http://51xuetongxin.com/bbs/) | Powered by Discuz! X2 |